
World Diabetes Day (WDD), observed annually on November 14, shines a spotlight on the global impact of diabetes. This year’s theme, “Breaking Barriers, Bridging Gaps,” emphasises the need for equitable, quality treatment and healthcare access for everyone diagnosed with diabetes. As diabetes cases surge worldwide, the campaign focuses on empowering people through early detection, testing, and awareness of risk factors.

The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is crucial in managing diabetes, as many individuals are unaware they have the condition until they experience serious complications. Routine screening and awareness about diabetes symptoms can lead to timely intervention, significantly improving long-term health outcomes.
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body struggles to effectively process glucose from food, due to insufficient insulin production or improper insulin use. Here’s an overview of the primary types of diabetes:
1. Type 2 Diabetes
In type 2 diabetes, the body does not produce enough insulin or fails to use it effectively, leading to insulin resistance. This type is the most common form of diabetes.
2. Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the body produces little to no insulin. Patients require insulin therapy to manage blood sugar levels and ensure survival.
3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes affects some women during pregnancy, and it elevates the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Recognizing the early signs of diabetes can prevent severe complications. Some common symptoms include:
- Increased thirst and dry mouth
- Unexplained weight loss
- Frequent urination
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue and numbness in hands or feet
- Slow-healing cuts or sores
- Frequent infections, such as yeast or skin infections
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several factors can elevate the risk of developing diabetes, including:
- Being overweight or having high adiposity
- Age 45 and above
- Family history of type 2 diabetes
- Inactive lifestyle
- Stress and metabolic liver disease
- Gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Diagnostic Tests for Diabetes
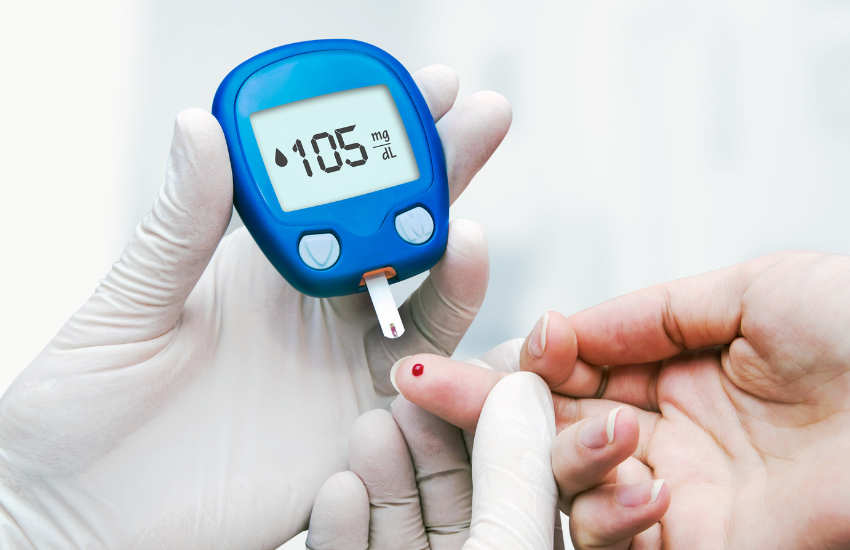
Three main tests help diagnose diabetes:
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test
- Postprandial Blood Glucose Test
- Glycated Hemoglobin Test (HbA1c) – which reflects the average blood glucose levels over three months.
Preventing and Managing Diabetes
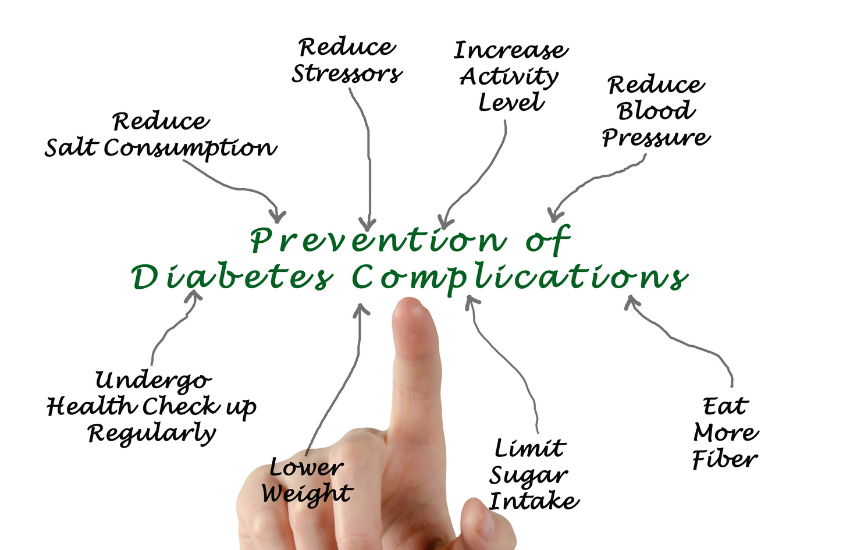
While genetic factors cannot be controlled, several lifestyle adjustments can reduce the risk of developing type 2 and gestational diabetes:
- Healthy Diet: Consume a balanced diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 40 minutes of moderate activity five days a week.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce insulin resistance.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques to reduce stress, a significant risk factor for diabetes.
- Healthy Sleep Cycle: Quality sleep supports metabolism and helps regulate blood sugar.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both contribute to complications and increased risk factors associated with diabetes.
Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
When left unmanaged, diabetes can lead to severe health complications such as cardiovascular disease, nerve and kidney damage, foot ulcers, dental problems, depression, and more. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding risk factors, and following preventive measures, individuals can lead healthier lives with diabetes.
World Diabetes Day: A Call to Action
As World Diabetes Day approaches, it is a reminder for communities, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to work together in breaking barriers and bridging gaps in diabetes care. Empowering people through knowledge, resources, and access to quality care can create a healthier future for everyone.
Also read: BMW 2 Series Gran Coupe Facelift: A Refreshed Rival to the Mercedes A-Class
